Managing an industrial facility is a crucial task and is the main way to make production activities run efficiently.
Industrial management uses various techniques, as well as the knowledge and innovation of professionals to optimize productivity and order in a facility.
An industrial facility cannot exist without management, as it would become a non-productive chaos that would gradually ruin the whole industry.
Why is an industrial facility management so important?
First of all, industrial management is important because it allows efforts, skills, and resources to be directed towards productivity and efficiency.
Industrial management is composed of a wide set of techniques that seek to minimize time, costs and losses, in order to increase the value of production.
Although management is generally associated with the industrial facility production, the truth is it also covers processes such as storing, organizing and distribution, all of which are activities closely associated to production.
Hay que resaltar que la gestión es útil para planificar y programar las reformas de naves industriales (y/o el mantenimiento), con el fin de no interrumpir o afectar a las actividades productivas.
Who is in charge of managing industrial spaces?
In production, industrial engineer are the main managers, since they have the knowledge, experience and professional training to apply the techniques correctly.

An industrial engineer is familiar with production processes. This is a professional trained to carry out industrial optimization.
However, it’s generally the managing directors who are in charge of managing an industrial facility.
A manager has to organize, plan and control activities additional to production, such as storing, distribution, etc.
Techniques to efficiently manage a facility
Currently there is a diversity of efficient industrial management techniques, some with a more traditional approach and others with a more modern and innovative attitude.
Modern techniques differ from traditional techniques because they leave a linear way of thinking behind, adopting a more dynamic and flexible way of understanding complex activities.
Of all the industrial management techniques, these are some of the most important:
5S Methodology
It is a technique of Japanese origin, consisting of a set of 5 stages based on oriental principles. Its name is due to the fact that the name of each of the 5 stages begins with the letter “S”.

Las etapas del método 5s son:
- Seiri: traducida como clasificación, esta etapa consiste en la identificación y diferenciación de los elementos necesarios y los inútiles para la producción.
- Seiton: esta etapa comprende el orden, por lo que básicamente consiste en organizar el espacio industrial, situando los elementos necesarios para la producción.
- Seiso: está vinculada con el orden y la limpieza del espacio industrial.
- Seiketsu: traducida como estandarización, es una etapa en la cual se previenen las anomalías, es decir, el desorden y la suciedad, fijando las normas y procedimientos adecuados para la producción.
- Shitsuke: por último la disciplina, una etapa en la que se fomenta el esfuerzo para seguir mejorando la actividad productiva.
Kaizen
This is another oriental technique, which stands out for its philosophy status. Kaizen is a word that means “improvement”.
Its main goal is to manage industrial quality through a continuous improvement process, consisting of simple and specific actions.
This technique considers the industry as a whole, in which every component (workers, managers, engineers, directors, etc.) has an active role in the search for continuous improvement.
Total productive maintenance (TPM)
It’s a Japanese technique that has also risen to a philosophy status. It consists of the elimination of loss of time (stoppages, standstills, interruptions, etc.), quality and costs during production.
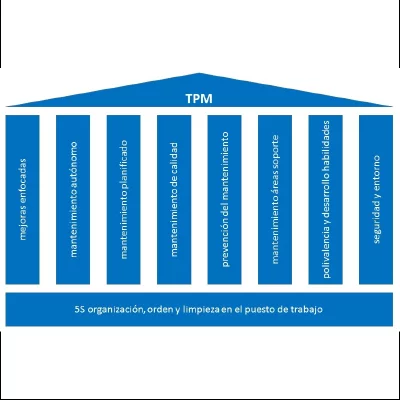
- Mejoras enfocadas: es un proceso de mejora continua que determina las bases, para así realizar los cambios pertinentes de forma planificada y precisa.
- Mantenimiento autónomo: conjunto de actividades realizadas por los operadores de maquinaria para preservar y acondicionar el estado de los equipos y máquinas.
- Mantenimiento planeado: actividades sistemáticas efectuadas para renovar el estado deteriorado de la maquinaria y de los equipos
- Control inicial: consiste en el aprendizaje de los errores para reducir el deterioro de los equipos y máquinas y disminuir los gastos de mantenimiento.
- Mantenimiento de la calidad: énfasis en el cumplimiento de las normativas y estándares de calidad.
- Entrenamiento: proceso de capacitación y preparación del personal laboral en las áreas profesionales respectivas.
- Mantenimiento productivo total en oficinas: se refiere a transferir todo el conjunto de mejoras industriales a los espacios de oficina.
- Seguridad y medio ambiente: consiste en el cumplimiento de las leyes medioambientales y de seguridad establecidas por el gobierno.
8D
Esta técnica está constituida por 8 disciplinas, las cuales estarán orientadas a la resolución de problemas. Es especialmente usada para afrontar inconvenientes en los controles de calidad.

The 8 disciplines of this method are:
- Formación de un equipo experto con conocimientos en diversos campos
- Definición precisa del problema
- Aplicar y comprobar una solución provisional
- Identificar la causa matriz del problema
- Determinar y examinar soluciones de corrección permanente
- Aplicar y verificar las soluciones correctivas permanentes
- Prevenir el resurgimiento del problema y/o sus causas
- Reconocer el esfuerzo del equipo
